As the global community intensifies its efforts to combat climate change, the energy sector is undergoing a significant transformation towards cleaner and more sustainable sources. Chevron, traditionally known for its oil and gas operations, is actively shifting its focus to embrace this new energy landscape. A testament to this commitment is Chevron’s involvement in the Advanced Clean Energy Storage (ACES) project in Delta, Utah. This ambitious initiative not only underscores the company’s dedication to lower-carbon energy solutions but also positions it at the forefront of the burgeoning hydrogen economy. By investing in cutting-edge hydrogen technology and infrastructure, Chevron aims to play a pivotal role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and fostering a sustainable energy future.
Table of Contents
ToggleBackground on the ACES Project
The ACES project is a landmark endeavour designed to revolutionize the way renewable energy is stored and utilized. Located in Delta, Utah—a region with unique geological features conducive to large-scale energy storage—the project was initially developed through a collaboration between Mitsubishi Power Americas and Magnum Development. Recognizing the project’s potential to significantly impact the energy sector, Chevron acquired a majority interest in ACES Delta, LLC, the joint venture overseeing the project, in 2023.
This strategic partnership brings together Chevron’s extensive expertise in energy production, Mitsubishi Power’s advanced technology in power generation, and Magnum Development’s specialization in energy storage solutions. The U.S. Department of Energy has also demonstrated strong support for the ACES project by issuing a conditional commitment for a $504.4 million loan guarantee. This federal backing highlights the project’s importance in advancing clean energy technologies and its alignment with national goals for reducing carbon emissions.
The primary objective of the ACES project is to convert surplus renewable energy—particularly from wind and solar sources—into hydrogen via electrolysis. This hydrogen can then be stored on a massive scale and dispatched as needed, effectively addressing the intermittency challenges associated with renewable energy sources.
Technology Behind the Project
At the core of the ACES project is the integration of renewable energy generation with advanced hydrogen production and storage technologies. The process begins with the use of a 220-megawatt bank of electrolyzers, which are devices that use electricity to split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen—a method known as electrolysis. The electricity powering these electrolyzers is sourced from renewable energy, ensuring that the hydrogen produced is “green” and contributes minimal carbon emissions.
Once generated, the hydrogen is stored in two expansive underground salt caverns, each with the capacity to hold up to 150 gigawatt-hours of energy. These salt caverns, formed naturally over millions of years, offer an ideal environment for hydrogen storage due to their structural integrity, impermeability, and scalability. The use of geological formations for energy storage is a proven technology, and in the case of hydrogen, it allows for the storage of large quantities of energy in a stable and secure manner.
This stored hydrogen serves as an energy reserve that can be utilized to generate electricity during periods of high demand or when renewable energy generation is low. By converting and storing excess renewable energy, the ACES project effectively creates a buffer that enhances grid stability and reliability. Moreover, the hydrogen can be transported and used in various sectors beyond power generation, including transportation and industrial processes, further amplifying its impact on reducing carbon emissions.
The technological approach of the ACES project addresses one of the critical hurdles in the widespread adoption of renewable energy—its intermittent nature. By providing a viable solution for large-scale energy storage, the project demonstrates how hydrogen can play a central role in transitioning to a low-carbon energy system.
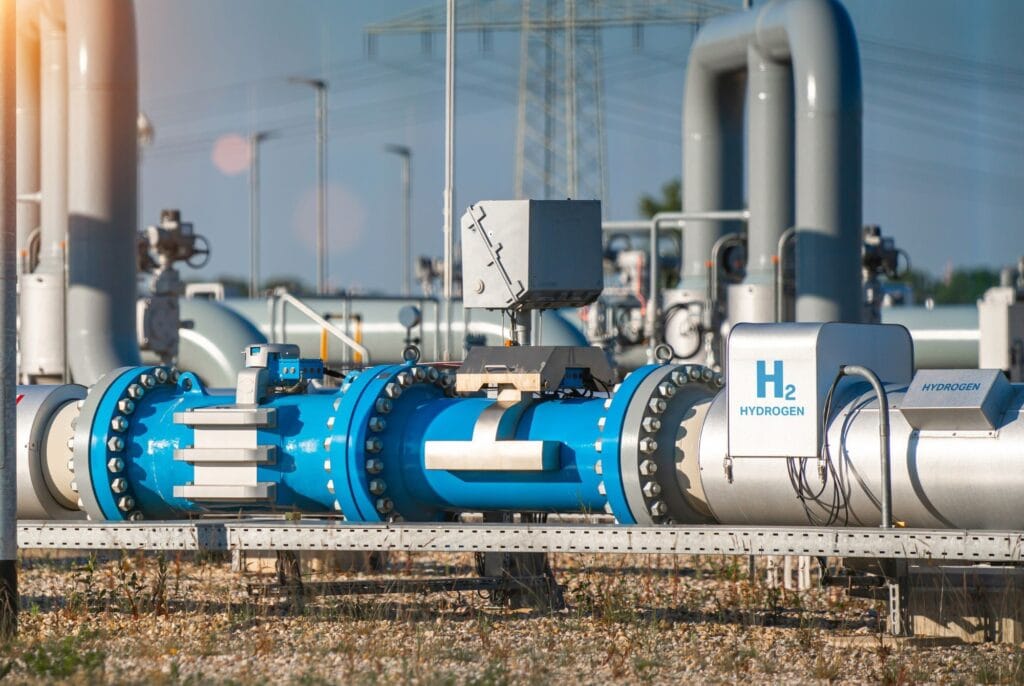

Chevron’s Role and Investment
Chevron’s engagement with the ACES project is part of a larger strategy to diversify its energy portfolio and reduce carbon emissions across its operations. In September 2023, Chevron U.S.A. Inc., through its Chevron New Energies division, acquired a majority stake in ACES Delta, LLC, which oversees the project. This acquisition not only underscores Chevron’s commitment to alternative energy sources but also highlights its strategic emphasis on hydrogen as a critical component of future low-carbon solutions.
Chevron New Energies is dedicated to accelerating the company’s entry into the hydrogen market, a sector increasingly seen as essential for achieving global decarbonization goals. With this investment, Chevron aims to leverage its experience in large-scale energy projects to advance hydrogen infrastructure and distribution capabilities across the western United States. Chevron CEO Mike Wirth, along with Austin Knight, the company’s Vice President of Hydrogen, has expressed that Chevron’s involvement in ACES represents a bold step towards building a cleaner energy future by harnessing the potential of hydrogen.
The Potential Impact of the ACES Project
The ACES project holds significant potential to reshape the energy landscape by advancing large-scale hydrogen storage and distribution. By converting renewable energy into hydrogen and storing it in massive salt caverns, the project addresses one of the most pressing challenges associated with renewable energy: intermittency. Stored hydrogen can be dispatched when renewable energy generation is low or during peak demand periods, thereby enhancing grid stability and supporting a resilient energy infrastructure.
Beyond power generation, the hydrogen produced at ACES has applications in various industries, from transportation to manufacturing. For instance, the Intermountain Power Project (IPP), a coal-fired power plant undergoing a shift towards cleaner fuels, will initially use this hydrogen to blend with natural gas, aiming for a complete transition to hydrogen by 2045. This shift could serve as a model for other power plants looking to reduce emissions and adopt cleaner fuels.
The environmental benefits of ACES are substantial, as the use of green hydrogen in place of fossil fuels can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions. In addition to positioning Utah as a central hub for hydrogen storage and distribution in the United States, the ACES project is likely to stimulate job creation, economic growth, and innovation in renewable energy technologies.
Challenges and Future Outlook
While the ACES project presents numerous advantages, it also faces certain challenges. The high cost of hydrogen production, particularly green hydrogen, poses a significant barrier to widespread adoption. Electrolysis is currently an energy-intensive process, and the scale of infrastructure required for effective hydrogen storage and transportation remains extensive. To make green hydrogen more competitive, technological advancements and cost reductions in electrolyzer technology will be crucial.
Policy support will also play a vital role in the project’s long-term success. Favorable regulations and financial incentives can help spur the growth of hydrogen infrastructure. The U.S. Department of Energy’s $504.4 million loan guarantee for ACES demonstrates a strong commitment to supporting projects that align with national decarbonization goals, but further governmental support may be necessary to overcome regulatory and economic hurdles.
Looking forward, the ACES project is expected to begin commercial operations by 2025, with a scalable model that could influence other regions and industries. As it progresses, the ACES project could pave the way for a broader hydrogen economy, with applications expanding across multiple sectors. By positioning hydrogen as a viable solution for large-scale energy storage and emissions reduction, Chevron and its partners in the ACES project are setting a precedent for future investments in clean energy. This project marks a pivotal step toward a resilient, low-carbon future that could redefine energy systems in the United States and beyond.
Conclusion
Chevron’s active participation in the Advanced Clean Energy Storage (ACES) project underscores its commitment to advancing hydrogen as a pivotal component of the future energy landscape. By leveraging its extensive expertise in energy production and distribution, Chevron is poised to play a significant role in the development and commercialization of hydrogen technologies. The ACES project not only addresses the intermittency challenges associated with renewable energy sources but also sets a precedent for large-scale hydrogen storage and utilization. As the project progresses towards its anticipated commercial operations in 2025, it exemplifies a strategic move towards a more sustainable and resilient energy system, aligning with global efforts to reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change.